|
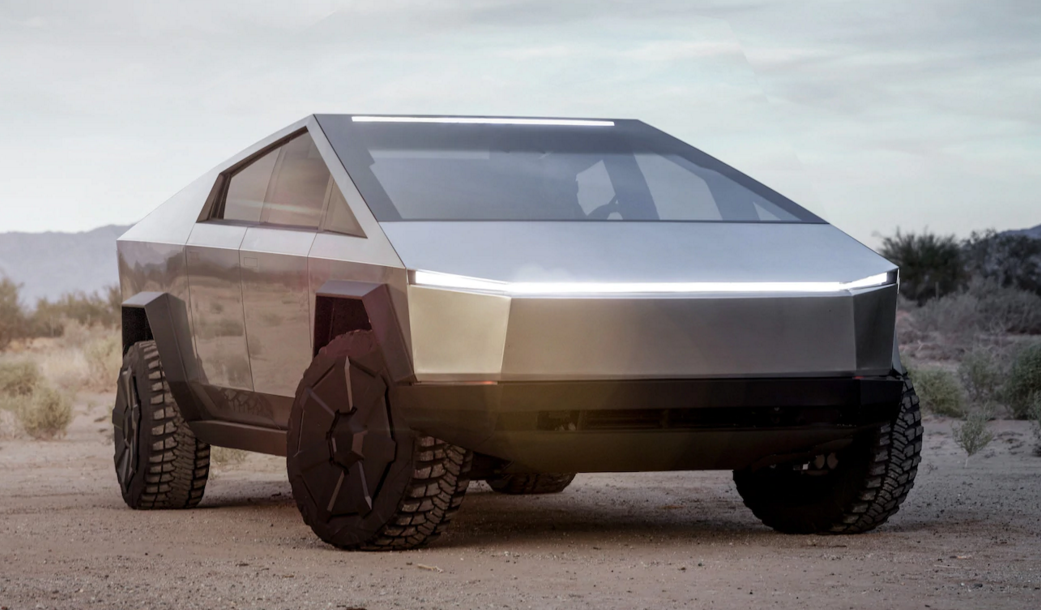
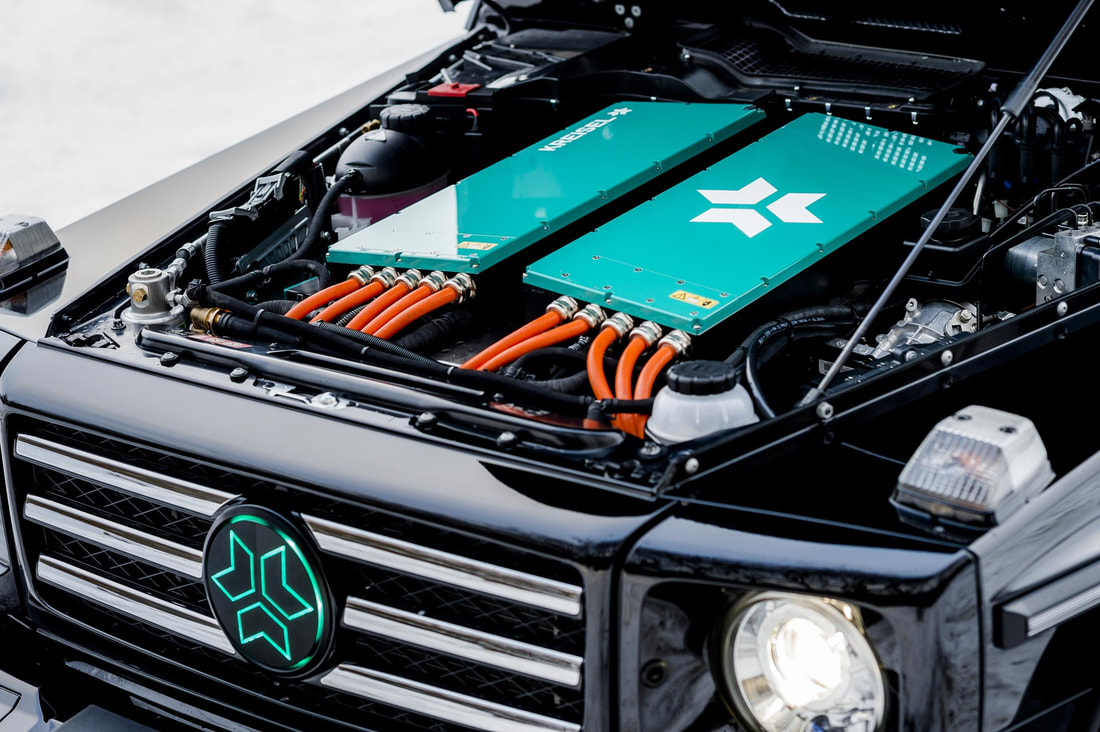
Since our last adventure most of our time has been spent trying to save the planet and the eco-systems we so dearly love and rely on. As every day passes the severity of the climate emergency we are in becomes more and more apparent. We dream of visiting the Amazon rainforest, but we fear that by the time we get there it might be gone! Every action has a carbon cost attached to it, which is making decisions very hard to make. Should we even continue our trip? Will we feel huge guilt by doing something so selfish when we should be fighting for the planet? How will we get to South America? Do we need to stop using Bee-bee because she runs on diesel? Is it feasible to use an electric 4x4 to overland the world? In this blog I’m going to focus on that last question. Is it feasible to use an electric vehicle to overland the world? The simple answer is yes. In 2017, our friends, Magdalena and Benedikt were the first to circle the Caspian Sea in an electric vehicle (Tesla Model S), from Switzerland to Central Asia and back via the Baltic countries. The “official” charging points finished in Croatia, forcing Magdalena and Benedikt to get “creative” adding a new dimension to an already tough overland trip. I had the pleasure of designing the vehicle graphics and interviewing them on The Overlanding Podcast. On the 7th of April 2019, The Plug Me In project finally reached Sydney from the UK after travelling for 1,119 days through 34 countries, covering 95,000km becoming the longest journey in an Electric Vehicle to date. So… It is possible, but... Is it greener to replace Bee-bee with an electric alternative? To calculate the carbon footprint of any vehicle is incredibly complex. The processes involved in getting raw minerals from the ground and made into a showroom ready vehicle are multifaceted and include many separate industries. Components have to be produced and often transported and then assembled. Every stage of the process requires energy and produces carbon, including the production of buildings and infrastructure (robots, phones, desks, etc). Once the vehicle has been built, the way it is used, how old it is and how well it has been maintained are all wildly erratic variables that affect the amount of carbon it produces. Luckily someone else has done most of the hard work for me. In his book “How Bad Are Bananas” – Mike Berners-Lee concludes that most new vehicles have a carbon footprint that equates to a monetary value. Berners-Lee suggests that a new vehicle will have a 720kg per £1000 that you spend on it. Unfortunately our vehicle isn’t new. Bee-bee is 26 years old and has a 3-Litre Turbo Diesel engine that has been well maintained. Typically, embodied emissions produced in the production of new cars equal the exhaust pipe emissions over the entire lifetime of the vehicle. Bee-bee is older than average. Berners-Lee deduces - “Generally speaking, it makes sense to keep your old car for as long as it is reliable, unless you are doing high mileage or the fuel consumption is ridiculously poor.” Essentially the longer you keep your vehicle the more the embodied emissions reduce per mile over time. On top of the Carbon produced by burning the fuel there is the carbon cost of getting the fuel out the ground, refining it and then shipping it around the world. Diesel engines are typically about 30% more efficient at turning fuel energy into vehicle movement. Unfortunately for us, each litre of Diesel has a slightly higher footprint (13 per cent) than petrol, but it produces a proportionately higher energy to compensate. Typically petrol is a cleaner option. Sadly diesel engines produce higher levels of microscopic particulates and nitrogen oxides and contribute massively to reductions in air quality that effect humans. These ultrafine particulates can penetrate deep into the lungs, causing irritation and can potentially trigger asthma attacks and cancer. According to Berners-Lee “Overall, it is hard to say which fuel wins as the environmental vehicle fuel”. What we do know is that both petrol and diesel are pretty terrible for the planet, with diesel being worse for humans. How does that compare with an electric vehicle? If the production of the vehicle produces about 50% of the total carbon footprint with exhaust pipe emissions making up the other half, does that mean that 50% of the total carbon footprint of an electrical vehicle is tied up in the production too? No, is the simply answer. Electric cars use lithium-ion batteries. The extraction of the exotic materials (lithium, cobalt, magnesium and nickel) used to produce those batteries creates hotspots in the vehicle manufacturing process. In a head-to-head comparison, electric vehicle production generates about 97% more carbon than a traditional combustion engine, with about 43% (the hotspot) of that being the battery. As technology advances these figures should reduce. Electric vehicles are charged by coal, gas and nuclear power stations, as well as some renewable sources, all of which have an associated carbon footprint. So that raises the question – how much of a carbon saving does an electric vehicle actually give you? Well thankfully, again, someone else has done the hard work for me. Volkswagen (who can definitely be trusted when it comes to telling the truth regarding emissions) carried out a like-for-like cradle to grave comparison between a pure electric e-Golf and a diesel-powered Golf TDI. Volkswagen concluded that “even in countries that are intensely reliant on coal-fired electricity, like China, a battery electric model will always pollute less CO2 than one with an internal combustion engine”. Even with the additional carbon produced during the production of the battery the typical saving is about 15%. This would be greatly increased if the electricity used for charging was sourced from renewables. That figure came as quite a surprise to me. I was expecting it to be a much higher saving. It is pretty much impossible to come to a definitive conclusion as to the carbon saving figure we would make by switching to an electric vehicle – we simply can’t compare like for like. It would be fair to say though that we wouldn’t be adding more carbon by switching, especially if that vehicle was second-hand. You only have to have a quick glance at the Electric Vehicle World Sales Database to realise the rate at which the sector is growing. As a result of the expanding electric vehicle market (and popularity of handheld devices), the demand for lithium is increasing exponentially. Between 2016 and 2018 Lithium doubled in price. Ironically, as the world clambers to replace fossil fuels with clean energy in an effort to clean up the planet, the consequences of extracting that much lithium is becoming a major issue in its own right. Toxic chemical leaks from Lithium mines have wreaked havoc with ecosystems and it’s predicting that, by 2050, the demand for the exotic metals essential for lithium-ion batteries may be in short supply. The lithium extraction process uses huge amounts of water, in Chile’s Salar de Atacama, mining activities consumed 65% of the region’s water. Lithium is not the only problematic metal used in producing batteries. Cobalt, unlike most metals, is classified as a toxic carcinogen and has been linked to cancer. It’s found in huge quantities across the whole of the Democratic Republic of Congo and central Africa and in recent years the price has quadrupled. These factors have resulted in unauthorised mines cashing in on the demand, resulting in unsafe and unethical methods of extraction, often using child labour, without the appropriate health and safety equipment and procedures. The final issue with lithium-ion batteries is what to do with them once they reach the end of their lifespan. They are incredibly difficult to recycle. Ironically when researching this blog post I discovered two companies, Voltra and Tembo, that make an electric 70 series Landcruiser… wait for it… to be used in mines that excavate coal. It is common knowledge that the world would be a much better place if fossil fuels were left in the ground. Where’s Alanis Morissette when you need her!? “Voltra provides underground mining fleets with the durability and toughness of the original 79 series Land cruiser, but with zero emissions, significantly reducing a mine’s carbon footprint”. Being an environmentally conscious overlander is hard work. Making the correct decisions to limit your own impact on the world is a minefield of complicated sums and moral dilemmas. Is there even a suitable vehicle that could replace Bee-bee? The market for off-road electric vehicles is currently slim. Telsa announced the CyberTruck last year. One part DeLorean, one part stealth bomber, it’s not the most attractive of vehicles and where would we put the rooftent? Elon Musk claims it’ll have a +500 Mile range, he also claimed it was bulletproof. At it’s big reveal, Telsa’s head of design, Franz vol Holzhausesn threw a metal ball at the windows to demonstrate how tough it was, embarrassingly the glass broke. With a price tag of +$60,000 for the all wheel drive tri-motor version and a release date of 2022 it’s highly unlikely to happen for us! The most likely contender to populate the electric overland market is the Rivian R1. With a +400 mile range and some smart design Rivian are aiming for a market they understand. The Rivian R1 will be available as a pick-up and 7 seater station-wagon, has a wading depth of nearly a metre, up to 750hp, advanced traction control, a low centre of gravity and an incredible 0-60 time of 3 seconds. With independent motors operating each wheel it can even perform 360 degree “tank turns”. Again, with a price tag of +$60,000 and a pre-order waiting list I think we can cross this one off our list. Some companies offer conversions for existing 4x4’s. For the traditionalist, Plower in Holland can build you an electric Land Rover Defender. In Germany Kreisel can build you a fully electric G-Class.
As all these vehicles are well out of our price range we find ourselves asking the question again - Is there a suitable vehicle, which could replace Bee-bee and appease our demand to see the world with as little impact on the planet as possible? Yes… a bicycle.
0 Comments
|
Archives
July 2020
Categories
All
|
Proudly powered by Weebly








 RSS Feed
RSS Feed